A 2000 behavioural experiment by psychologists Sheena Iyengar and Mark Lepper showed that too many choices can cripple consumers’ ability to make a buying decision. When presented with 24 options at a simulated jam testing, only 3% of consumers made a purchase. By comparison, when the number of jars was reduced to 6, the percentage of buyers grew to 30%.
The Jam Experiment offered a momentous psychological insight into consumer buying behaviour and its findings are particularly relevant today. When customers are faced with a virtually unlimited number of choices in the globalised digital market, e-commerce and retail brands need to invest extra effort to build authentic experiences and stand out.
To successfully do that, they need to understand their buyer’s purchasing patterns and the growing variety of factors influencing their decisions in the digital economy.
Understanding the basic consumer buying patterns

Rather than assuming online users’ buying patterns and preferences, e-commerce and retail brands need to research and analyse their most common behaviours. The knowns of purchasing psychology and behavioural economics offer a good starting point for customer segmentation and marketing strategy planning.
Nielsen Norman Group identifies 5 types of shoppers in e-commerce:
1. Product-focused shoppers – goal-oriented buyers who want to make a purchase quickly. They typically research multiple websites to make a quick comparison of product features and pricing before buying. To win this customer, brands should provide detailed product descriptions and enable a streamlined checkout.
2. Browsers – consumers who continuously follow the latest trends and offers. They make a purchase when a particularly interesting opportunity is presented to them. E-stores should provide them with additional purchase options, easy access to new items, and the ability to share their thoughts on the product.
3. Researchers – doing in-depth research on the available options before they buy. They will most likely visit your website multiple times, and pay attention to product descriptions, images and user reviews. They are most likely to convert when presented with clear product features, product comparisons and user recommendations.
4. Bargain hunters – these types of buyers are looking for coupons, discounts and special offers. The more of these you offer to them, the greater the chance they will become repeat buyers.
5. One-time shoppers – usually people who bought a product thanks to a gift card or a coupon. They have no intention of coming back, so they will be looking for checkout without registration. However, brands that tactically use conversational commerce and engage them across additional channels may win them back.
While this segmentation provides a useful framework for understanding common consumer buying patterns, their decisions still depend on a variety of personal, psychological and social factors. And it is precisely these factors that have significantly changed in recent years.
Factors influencing buying decisions
The traditional marketing analysis recognises a number of factors that influence buying behaviours including geographic location, demographic properties, goals and motivations, as well as community recommendations. However, the hyper-connected digital consumer may no longer care about brick-and-mortar store locations as long as they are presented with flexible delivery options. Similarly, hybrid and remote workers may prefer food delivery options over dining out.
1. Buyers put novelty before loyalty.
The increased tendency to switch brands seems to be a long-lasting remnant of the pandemic economy. The 2022 Customer Pulse report by McKinsey confirms that consumers continue to abandon brands they have a relationship with in favour of those who offer better value and novelty. This behaviour was first identified in 2020 when 75% of US consumers said they tried a new shopping behaviour, with 36% of them trying a new brand or product.
Fast forward to 2023, consumers are still ready to make the switch for a better deal (66%), better product quality (58%), and better customer service (48%).
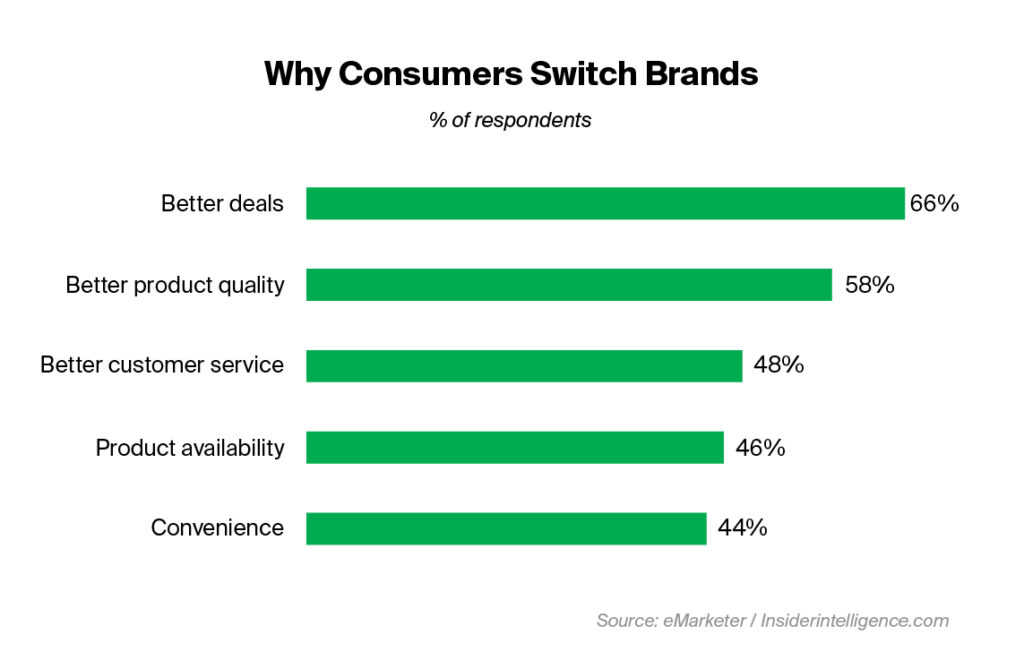
Pro tips: McKinsey suggests that brands should focus on introducing innovation and creating offers with a perception of better value to win (back) customers faster. On the other hand, any steps at communication personalisation through new conversational channels such as AI Chatbots, SMS Messages, WhatsApp Business Messages or Viber conversation suite may help strengthen brand loyalty with existing customers.
2. Convenience and sustainability are top shoppers’ priority lists
Another insightful study on consumers’ changing habits and priorities was published in 2022 by American Express. Having surveyed 2,000 UK adult consumers, it identified four types of shoppers: Practical Purchasers, Savvy Spenders, Sustainable Shoppers and Experience Seekers. Some of the key themes that emerged from this research are convenience and sustainability as new factors influencing purchasing decisions.
Convenience remains the top priority for 88% of the practical shoppers who want easy checkouts, Open Banking payment abilities and subscription options. As opposed to them, a whole new group of shoppers shows high awareness of climate issues and prefers to buy from brands that offer sustainable delivery options or that have a visible certification that the product is sustainably sourced.
Pro tips: To build streamlined buying experiences for your practical shoppers, make sure you include different payment methods, as well as an intuitive checkout. For sustainable shoppers, highlight any certifications or eco standards you follow.
3. Tailored communications increase brand loyalty.
Online consumers increasingly expect personalised offers to help them navigate the complex ecosystem of choices. According to a 2022 report by 3radical, 54% of buyers are willing to exchange personal information for tailored offers and promotions. However, brands often fail to meet their expectations. Only 18% of respondents strongly believe they have received customised recommendations and 65% reported receiving irrelevant offers.
The implications for brands that fail to offer customised experiences are alarming. 42% of buyers would be less inclined to shop with brands that did not extend tailored communications.
Pro tips: Brands should use advanced data analysis and clustering methodologies to better segment their audiences and provide more targeted offers. The communication medium is another important factor to consider. By reaching out to your consumers via their preferred channels such as SMS, chatbots, email or messaging apps, you can take personalisation to a new level.
4. Authentic experiences drive more purchases.
As shoppers become increasingly overwhelmed with offers from different brands, they are more likely to repeat purchases with the ones that provide distinctive value. According to Stackla report from 2021, 83% of respondents expect more authentic shopping experiences and one of the key types of content that enable that is user-generated videos and reviews.
This trend might be driven by the rising influencer economy, so it is reasonable to expect that more buyers will require authentic and interactive content from brands.
Pro tip: Offer your loyal customers a discount code or gift voucher if they leave a positive review or make a photo with your product. This type of content can be displayed on your website and social media profiles, as well as a variety of review sites your consumers might be visiting.
5. Convenient communications are an opportunity to delight.
The flexibility of online shopping has significantly extended over the past few years. Messaging apps have become the primary channel for personal communications and are increasingly expected to be used by brands as well. Earlier research suggested that 68% of respondents would take into account the convenience of communications when deciding on a purchase.
The study showed that consumers rate the brand’s ability to quickly resolve questions or issues as the most important feature when interacting with them. The close second is the ability to contact them via the method they prefer.
Pro tip: By expanding their communication strategy to include more channels such as messaging apps and AI chatbots, eCommerce and retail brands can build smarter customer journeys and provide more memorable experiences.
Conclusions
The psychology behind consumer buying behaviour offers essential insights for brands looking to tailor their offers to their consumers’ needs. In addition to the historical insights into purchasing patterns, brands should also consider the latest social and economic trends that are changing consumers’ decision-making processes.
E-commerce and retail brands that can quickly and successfully adapt to emerging trends and demands are more likely to see success than organisations resisting change.

